The COVID-19 pandemic, which has left its mark on our country over the last five years, has drawn the attention of scientists regarding the relationship between cancer and the disease. The pandemic has caused significant damage to individuals whose immune systems have been suppressed due to cancer or cancer treatment. Mortality rates have increased among cancer patients with suppressed immune systems during the pandemic.
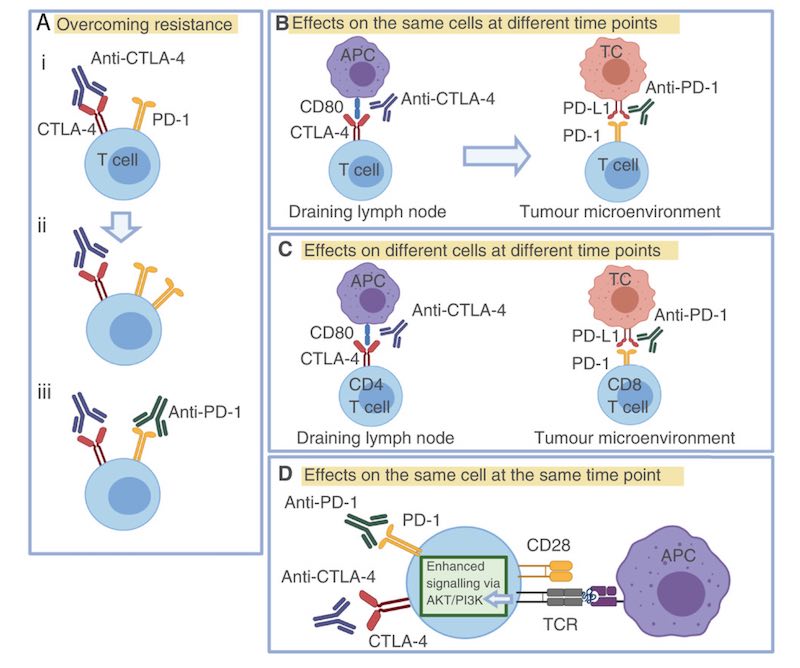
In the last 10 years being a part of it is the relationship between human cancers and immune system. Cancer cells escape from the immune system PDL-1 and CTLA-4 as such, certain histocompatibility antigens.
This relationship is known to be generated in this way is a guideline for the treatment steps at the same time. This treatment is called immunotherapy protocol. Especially PDL-1 and CTLA-4 many of inhibitor drugs is starting to become a part of cancer treatment.
The relationship between cancer and the immune system, microorganisms not only a well-known fact. HPV, EBV, HBV, HCV, HIV, HTLV oncogenic viruses such as viruses that cause cancer are among the known. Also called Helicobacter bacteria are also oncogenic between microorganisms is located.
Suppression of the immune system, promotes the formation of cancer. However, the immune system raises factors or anti-oncogenic (cancer formation) investigation of the presence of microorganisms is located in the research topics of the scientific community recently.
COVID-19 pandemic, given the relationship between cancer, cancer death rates in immunocompromised patients has been observed during the period artttigi pandemic.
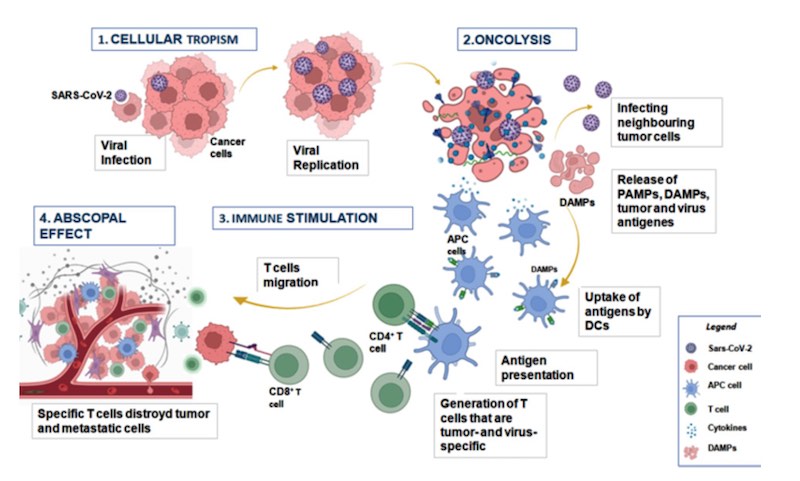
However, a recent study demonstrated that the COVID-19 pandemic in 16 cancer patients cancer without any treatment decreased. COVID-19 after infection 14anti-SARS-CoV-2 after vaccination 2 spontaneous regression occurred in cancer research that have been demonstrated in cancer patients.
COVID-19 infection still remains unanswered many questions about the impact on cancer. Patients with blood cancer and especially lung cancer has been adversely affected by the pandemic.
The reason for this is both cancer and COVID-19 stems from the negative influence on lung, and blood cells.
However, malignant tumors and is the deadliest of COVID-19, despite the increased risk following cancer-specific treatment, without some spontaneous cancer remission has been reported.
Following a viral infection, a newly diagnosed cases of clinical regression of the tumors is not knowledge. Information on the beneficial effects of viral infection, the first influenza (flu) in patients with leukemia and lymphoma who are infected with the virus is the information that is spontaneous regression.
COVID-19 can neutralize the Natural History of the disease, whether or not cancer has not been investigated systematically. COVID-19. the effect of the impact on a better understanding of the mechanisms of immunogenic cancer, will help you to optimize treatment strategies for such patients. This decline began to attract the attention of the scientists.
This is about 2 hypotheses have emerged.
- The first hypothesis of immune responses and cytokine storm that occurs after a viral infection in the tumor's immune system creates to be protected from the micro-environment that can destroy tumor cells overcoming hypothesis.
- The second hypothesis of the virus to infect the lungs and cause death in normal cells or cells such as blood cells, they are not.
In both hypotheses, a lot more supportive studies are needed.
However, it's hard to remove it from here.
In the years ahead oncogenic (cancer-causing) viruses so anti-oncogenic (cancer prevention) or the treatment we will start talking about viruses we will use.